
Car Registration Fee
Detailed guide to calculating the registration fee for imported cars. Understand all the factors that affect the cost.


A significant part of the cost of importing a car is the registration fee. Calculating it is a complex process because the exact amount is influenced by many parameters, which are:
It is the pre-tax price at which an identical, in terms of equipment, car was sold in Greece on the date of the first release of the car for import. This price is the price we pay when we import the car, that is, it is independent of the purchase price of the car.
Car taxation is graduated with a different customs clearance rate depending on the value, as we see analyzed below:
For value from 0 until 14.000 € with customs clearance rate 4%
For value from 14.000 € until 17.000 € with customs clearance rate 26%
For value from 17.000 € until 20.000 € with customs clearance rate 53%
For value from 20.000 € until 25.000 € with customs clearance rate 62%
For value from 25.000 € until 30.000 € with customs clearance factor 71%
For value from 30.000 € and above with customs clearance rate 30%
This means that a car with a pre-tax retail value of €15,000 is taxed up to €14,000 at the rate of €14,000 (4%) and for the remaining €1,000 at the rate of the category €14,000-17,000 (26%).
The registration tax rate that a car must pay increases for cars with older anti-pollution technology than that considered the most modern.
At this moment as first anti-pollution category are considered euro6 cars with first registration INDICATIVELY from 31/8/2018 to date.
For value from 0 until 14.000 € with customs clearance rate 4%
For value from 14.000 € until 17.000 € with customs clearance rate 26%
For value from 17.000 € until 20.000 € with customs clearance rate 53%
For value from 20.000 € until 25.000 € with customs clearance rate 62%
For value from 25.000 € until 30.000 € with customs clearance rate 71%
For value from 30.000 € and above with customs clearance rate 30%
In the second antipollution category Cars that belong to the Euro6 category and have a first registration certificate are classified INDICATIVELY from 31/8/2015 to 31/8/2018 with customs clearance rates being increased by 50%, so they are formed as follows:
For value from 0 until 14.000 € with customs clearance rate 6%
For value from 14.000 € until 17.000 € with customs clearance rate 39%
For value from 17.000 € until 20.000 € with customs clearance rate 79,5%
For value from 20.000 € until 25.000 € with customs clearance rate 93%
For value from 25.000 € until 30.000 € with customs clearance rate 106,5%
For value from 30.000 € and above with customs clearance rate 45%
In the third category Cars that belong to the euro6a or euro5b category and first registration are classified INDICATIVELY from 31/12/2012 to 31/8/2015, with the customs clearance rates being increased by 100%, so they are structured as follows:
For value from 0 until 14.000 € with customs clearance rate 8%
For value from 14.000 € until 17.000 € with customs clearance rate 52%
For value from 17.000 € until 20.000 € with customs clearance rate 106%
For value from 20.000 € until 25.000 € with customs clearance rate 124%
For value from 25.000 € until 30.000 € with customs clearance rate 142%
For value from 30.000 € and above with customs clearance rate 60%
In the fourth category Cars belonging to the Euro5a category with a first registration from 31/12/2012 and below with customs clearance rates being increased by 200%.
Finally, in addition to the registration fee, cars with Euro4 anti-pollution technology are subject to an environmental fee of €3,000, while cars with Euro5 anti-pollution technology are subject to an environmental fee of €1,000.
OBSERVATION:
The above does not mean that when we import a second generation Euro6 car we will pay more customs duty compared to a third generation Euro6 car. The reason is that the second generation Euro6 will be cleared with a higher customs clearance rate compared to the third generation Euro6, but it will have a greater impairment due to age and may ultimately result in lower customs duty.
The emitted mass of carbon dioxide will affect the registration fee coefficient, which will increase with increasing grams according to the list below:
3.1 For cars with first registration before 1/1/2021
3.2 For cars with first registration after 1/1/2021
Each month of circulation depreciates the value of the vehicle, while the depreciation rate is different depending on the type of body. Below is a summary table of depreciation per half-year, the depreciation actually occurs month-by-month, so there are intermediate values between those in the table below, which are briefly mentioned in six-month increments.
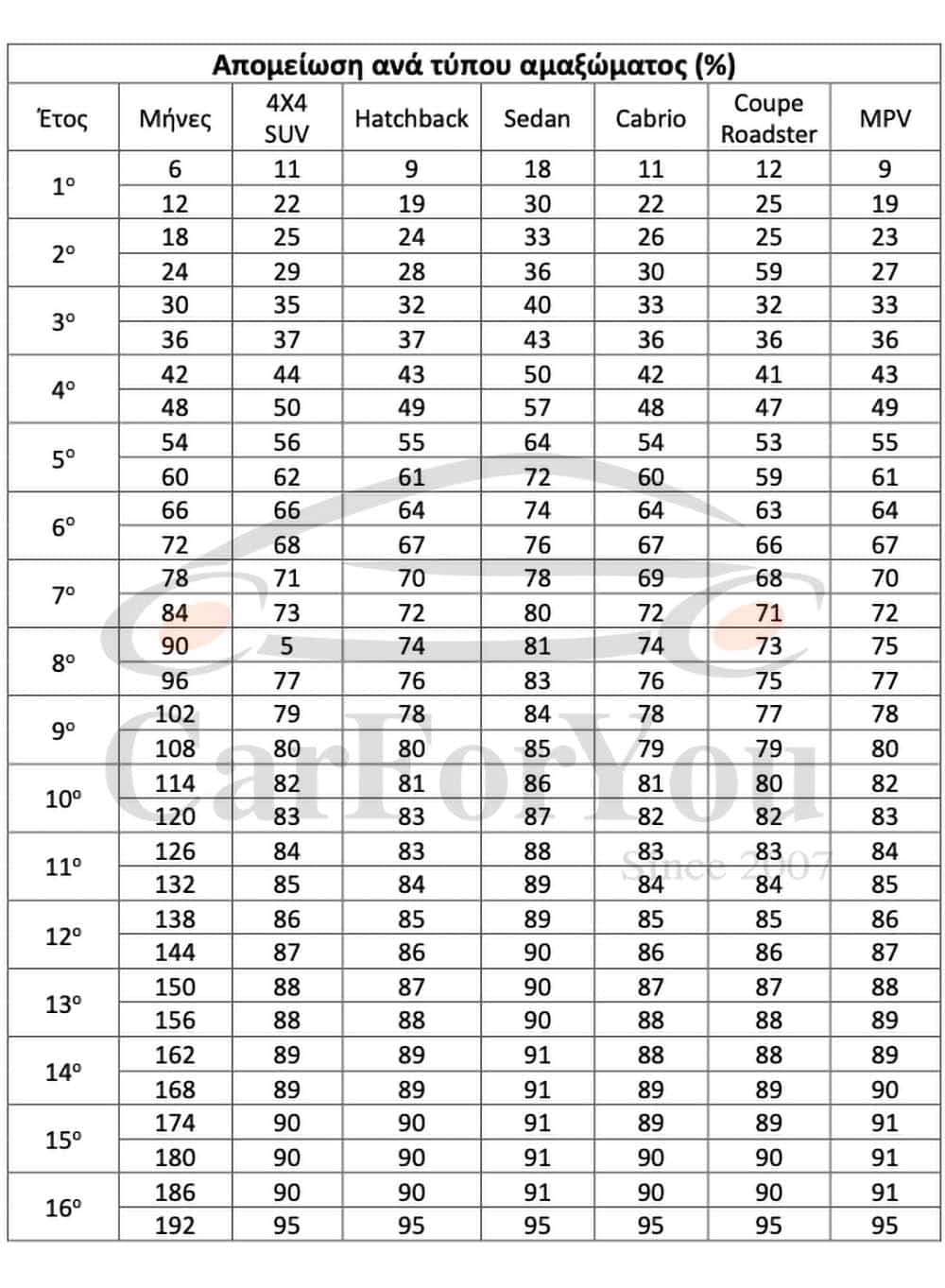
According to Greek law, each car travels an average of 15,000 km/year. For every 500 additional kilometers from the 15,000 average, its taxable value is reduced by 0.1%. The depreciation based on the kilometers traveled must not exceed 10%. To be more specific, the following tables give us the coefficient through which the amount that the car will be required to pay upon import will be calculated. The calculation of any depreciation of the registration fee that may arise due to kilometers is based on the kilometers indicated on the purchase invoice of the car, upon import of the car, and not the kilometers indicated on the odometer.
In other words, if we buy it with X kilometers, transport the car by road and finally import it with X+2,000 kilometers, then when calculating its registration fee, customs will take into account the kilometers indicated on the invoice and not the final kilometers that it will have on the odometer.
Motorhomes pay a quarter of the customs duty they would pay if they were just passenger cars.
VAT:
Used cars pay VAT either in the country of export or in the country of import. In the case of importing cars, it is in our interest that VAT is paid in the country with the lowest VAT, since in the case of cars it is not refunded to the buyer. New cars are required to pay VAT in the country of import. New cars are considered to be cars with less than 6,000 kilometers. and first registration certificate less than 6 months old. Both of these conditions must apply, i.e. if a car is 7 months old and 5,000 kilometers old or if it is 10,000 kilometers old and 5 months old, then it is considered new in both cases.
In the event that someone pays VAT on a new car in the country of purchase and then imports it, they will be required to pay it back with 24% on the net purchase price of the car, while they will not get the VAT paid back from the country of purchase.
The price at which a similar car was sold in Greece on the date of first release.
Cars with older anti-pollution technology have increased coefficients.
Grams of carbon dioxide affect the final tax rate.
Each month of circulation reduces the taxable value of the car.
31/8/2018 – Today
Basic factors
31/8/2015 – 31/8/2018
+50% on the basics
31/12/2012 – 31/8/2015
+100% on the basics
Before 31/12/2012
+200% on the basics

Not subject to registration fees

They pay half the registration fees

They pay a quarter of the fees

They pay a quarter of the fees
Automobile VAT:
Impairment:
Environmental Fees:
CO2 Additional Fees: